World
Health Organization Declares H1N1 Influenza Has Reached Pandemic Level By
Liz Highleyman
 On
June 11, 2009, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared that the ongoing outbreak
of influenza
A - H1N1 -- formerly dubbed swine flu -- has become a pandemic. The agency
raise the pandemic alert level from 5 to 6 (its highest level) after an emergency
meeting of infectious disease experts. On
June 11, 2009, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared that the ongoing outbreak
of influenza
A - H1N1 -- formerly dubbed swine flu -- has become a pandemic. The agency
raise the pandemic alert level from 5 to 6 (its highest level) after an emergency
meeting of infectious disease experts. Importantly,
a level 6 pandemic means sustained person-to-person transmission of an infectious
disease within multiple regions of the world -- it does not indicate anything
about the severity of disease. To date, the H1N1 flu still appears to be a relatively
mild illness, with a mortality rate comparable to or lower than that of a typical
seasonal flu. The last influenza pandemic -- due to the Hong Kong flu -- was declared
in 1968. In
the U.S., most H1N1 flu deaths have occurred in people with underlying health
problems. Pregnant women and people with compromised immunity -- which includes
HIV positive people -- are at increased risk for severe disease. So far, this
flu has infected a greater proportion of young people than usual, suggesting older
individuals born before 1957 may have some residual immunity from a past flu outbreak. | 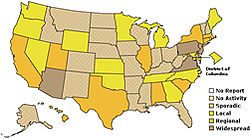 |
H1N1
continues to spread in North America, Europe, and Asia, but the southern hemisphere,
including Australia, is of particular concern since flu outbreaks are typically
worse during the winter.
The primary effect of the WHO declaration is
that it will trigger countries (whether or not they have reported any cases) to
implement disease control plans, though many have already done so.
According
to the latest WHO statistics, there have been 27,737 confirmed cases of H1N1 flu
in 74 countries, with 141 deaths. In the U.S., as of June 5, the Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention (CDC) has tallied 13,217 cases (affecting all 50 states,
Washington, DC, and Puerto Rico), with 27 deaths. For
further information, including the latest statistics and tips for flu prevention,
see the CDC's H1N1 influenza web site at www.cdc.gov
and the WHO flu web site at www.who.int.  Previous HIVandHepatitis.com H1N1 influenza coverage:
Previous HIVandHepatitis.com H1N1 influenza coverage:
CDC
Issues Flu Treatment Guidelines and Public Health Service Updates Antiretroviral
Therapy Recommendations for Pregnant Women with HIV
(May 29, 2009) H1N1
Swine Flu Update and CDC Interim Guidance for Clinicians Treating People with
HIV
(May 3, 2009) U.S.
Declares Public Health Emergency as Swine Flu Outbreak Spreads
(April 28,
2009)
6/12/09 Sources Centers
for Disease Control and Prevention. H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu). Updated June 10,
2009. World
Health Organization. Influenza A(H1N1). Updated June 11, 2009. CNN.
WHO declares swine flu pandemic. June 11, 2009.
|